Rocket Science
Rocket Science
ULA launches missions to space aboard its Vulcan and Atlas V rockets, including weather, telecommunications and national security satellites that protect and improve life on Earth, astronauts to the International Space Station, spacecraft to deep space and interplanetary exploration missions that further our knowledge of the universe. Rockets play an important role in our lives. Without rockets, we wouldn't be able to use our cell phones, find out the weather forecast, navigate with Global Positioning System (GPS), or explore our solar system—just to name a few.
Here's how it works—at liftoff the rocket’s powerful main engine starts and produces thrust. Thrust accelerates the rocket, with its payload, away from the launch pad. A typical rocket produces more than a million pounds of thrust that allows it to carry more than 6,000 pounds at speeds topping 22,000 miles per hour. This is equivalent to the power generated by 13 Hoover Dams, carrying the weight of eight horses, and traveling at speeds 15 times faster than a speeding bullet!
After leaving Earth's atmosphere, the rocket delivers its payload to the desired orbit, its desired trajectory or starts astronauts on their mission to the International Space Station. Once in the desired orbit, the spacecraft or payload can begin to do the work that makes all our lives easier and helps us to learn more about our planet, our solar system, and our universe.
STEM ACTIVITIES

Click here for additional challenge details and resources

Click here for additional challenge details and resources

Rocket Terminology
Jettison - to discard, to cast off
Liftoff - the instant when a rocket begins flight
Orbit - path of a satellite or spacecraft as it flies around Earth or another Planet
Satellite - object launch to orbit Earth or another planet
Spacecraft - craft capable of traveling in outer space
Thrust - the forward-directed force developed by a rocket engine
Trajectory - the path followed by an object moving through space
Downloads
Rocket Models
Cutaway Posters
Coloring Sheets
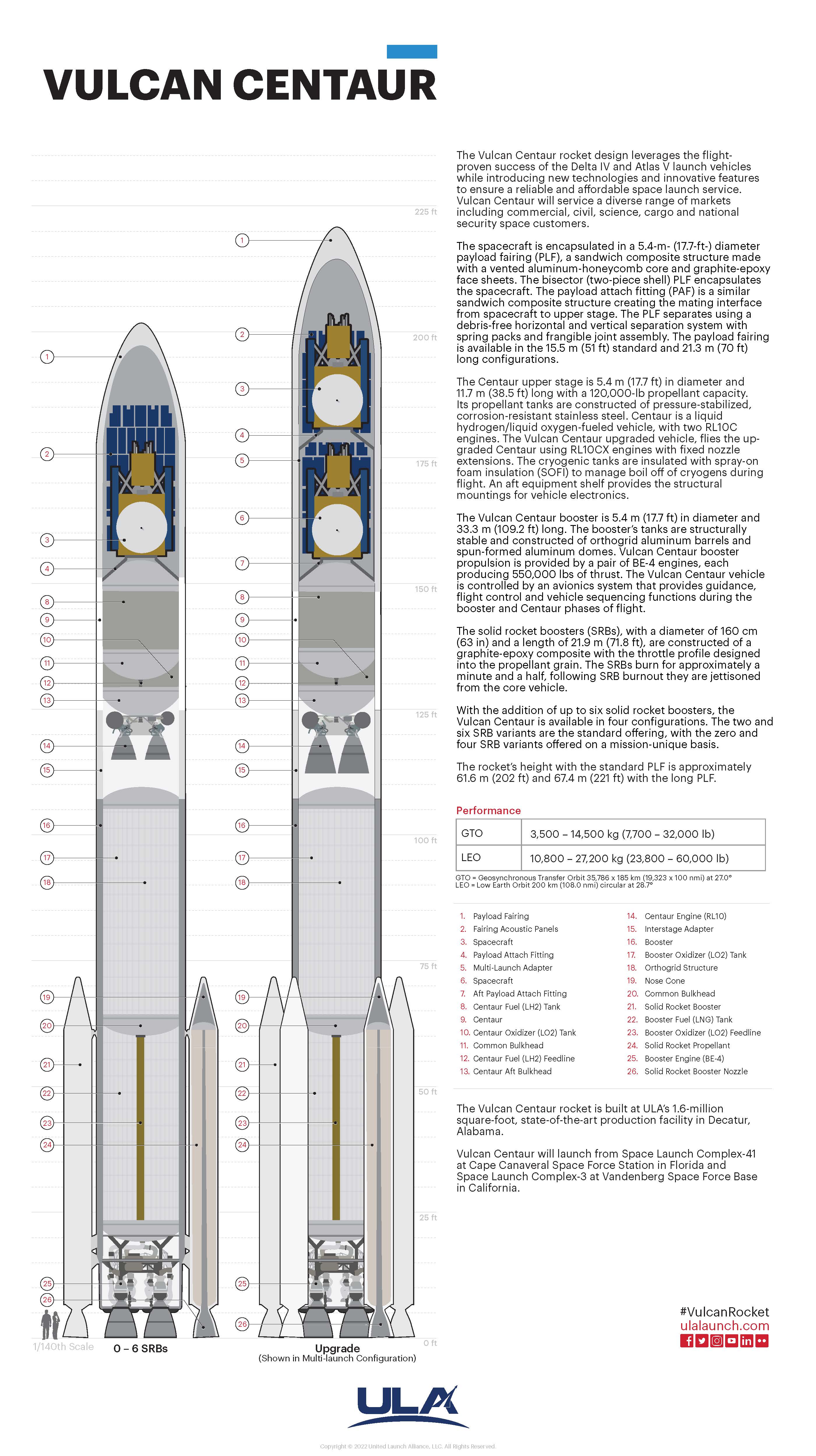
Vulcan Centaur
Delta II
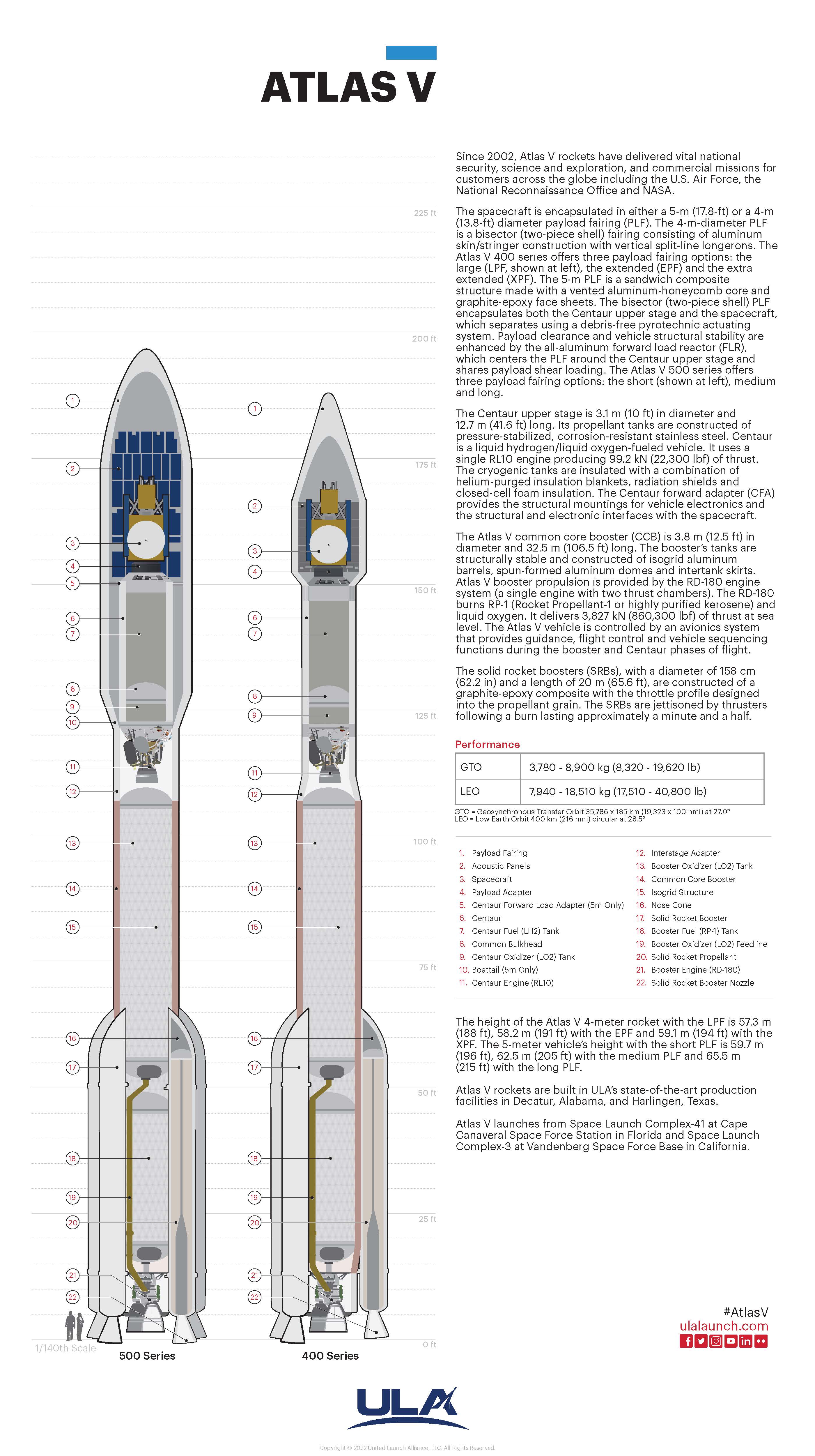
Atlas V Mars 2020
Atlas V Starliner
Atlas V Landsat 9
Atlas V Lucy
Artemis I SLS - ICPS
Activity Sheets
Rocket Science in 120
HOW BIG IS A ROCKET?
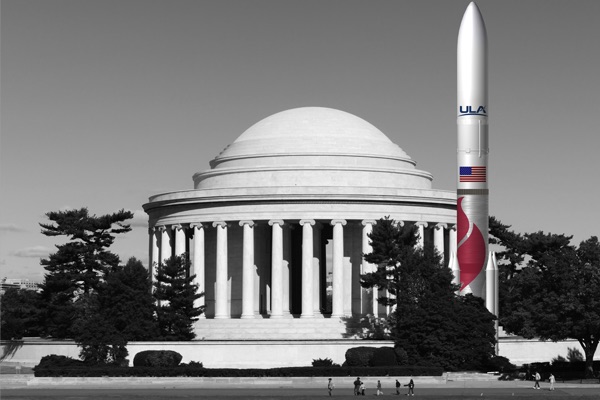

Vulcan Centaur comparison with the Thomas Jefferson Memorial in Washington, D.C.
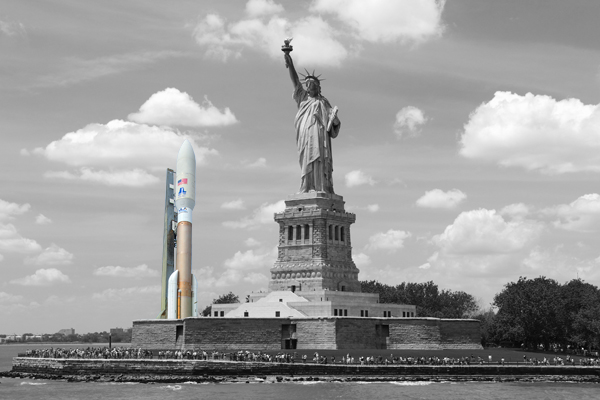

Atlas V comparison with the Statue of Liberty in New York City, NY.
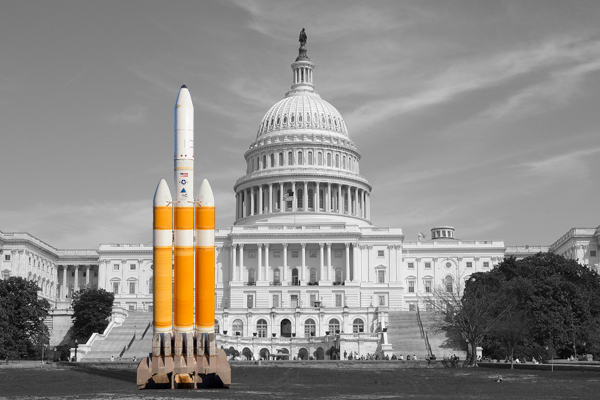

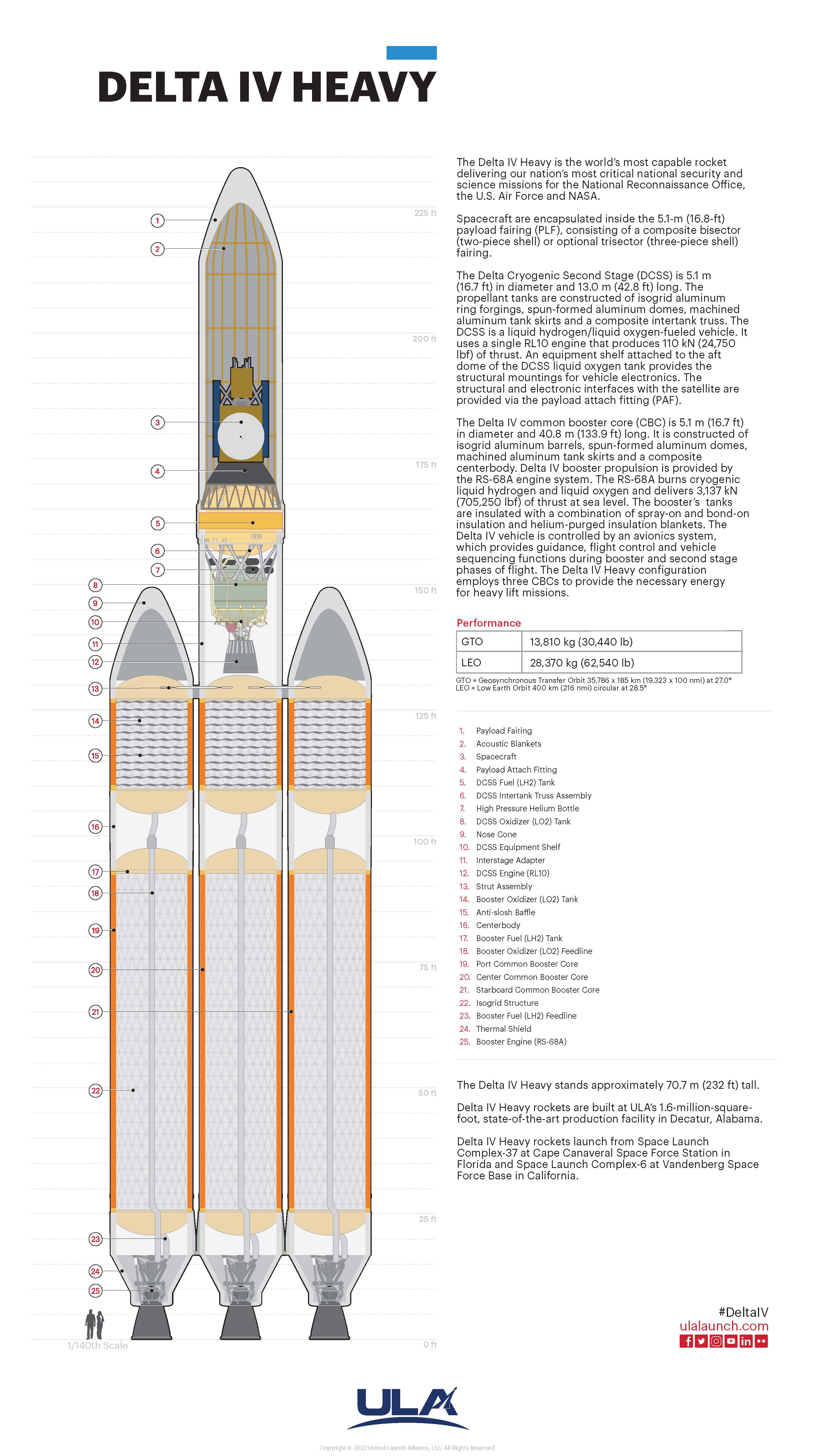
Delta IV Heavy comparison with the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C.
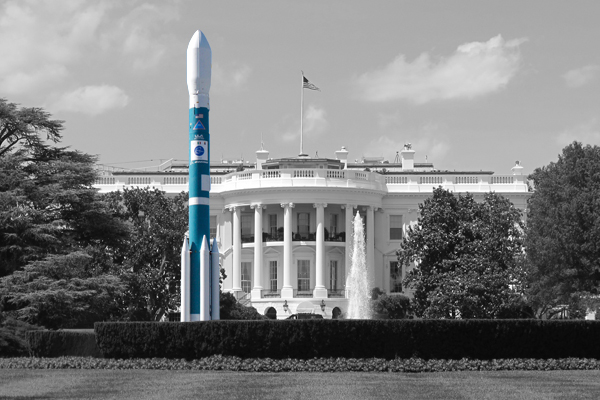

Delta II comparison with the White House in Washington, D.C.